Column: Europe’s future metals strategy hindered by current crisis
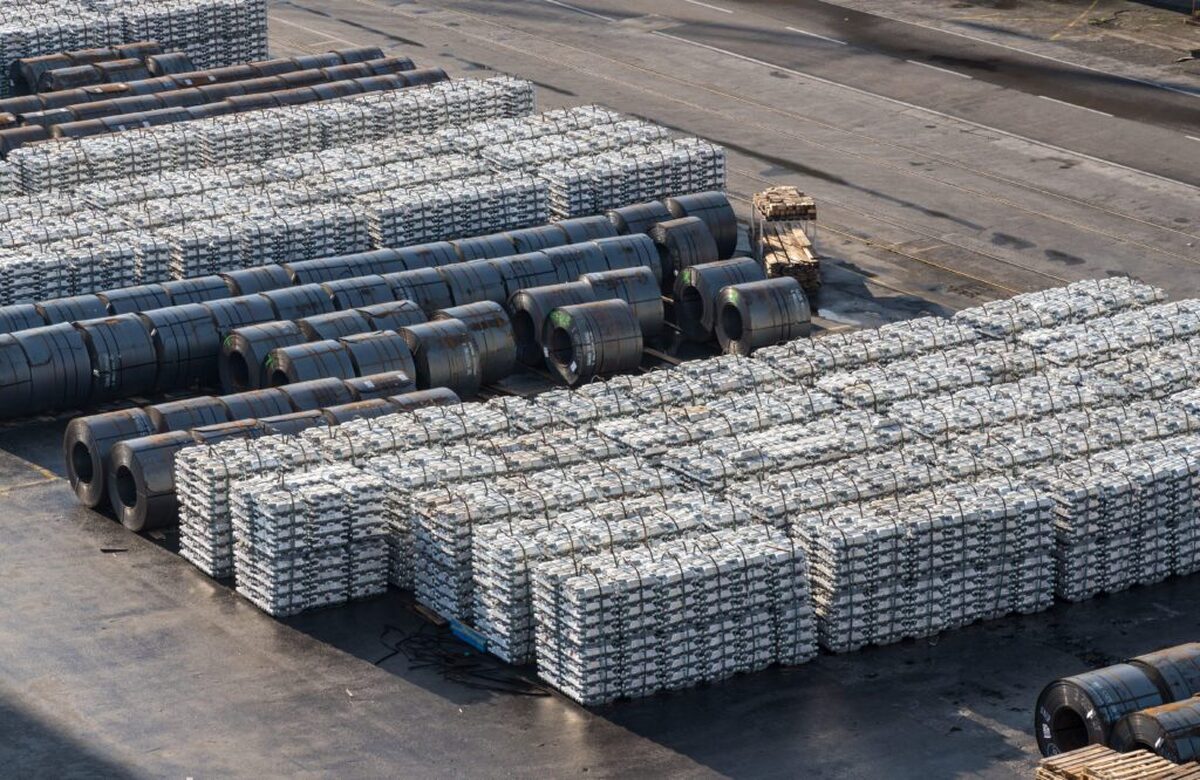

According to me-metals cited from mining.com, But even as European policymakers work to build a future industrial base, they are facing a crisis in the region’s existing metals sector.
Chinese over-capacity and high energy prices have accelerated the long-term decline of European steel and aluminum production.
The latest threat, however, is coming from the United States. President Donald Trump’s tariffs, particularly the increased tariff on aluminum imports, risk displacing a flood of metal into Europe.
Europe’s response is shaping up to be equally protectionist, heralding more fracturing of global trade patterns.
Building for the future
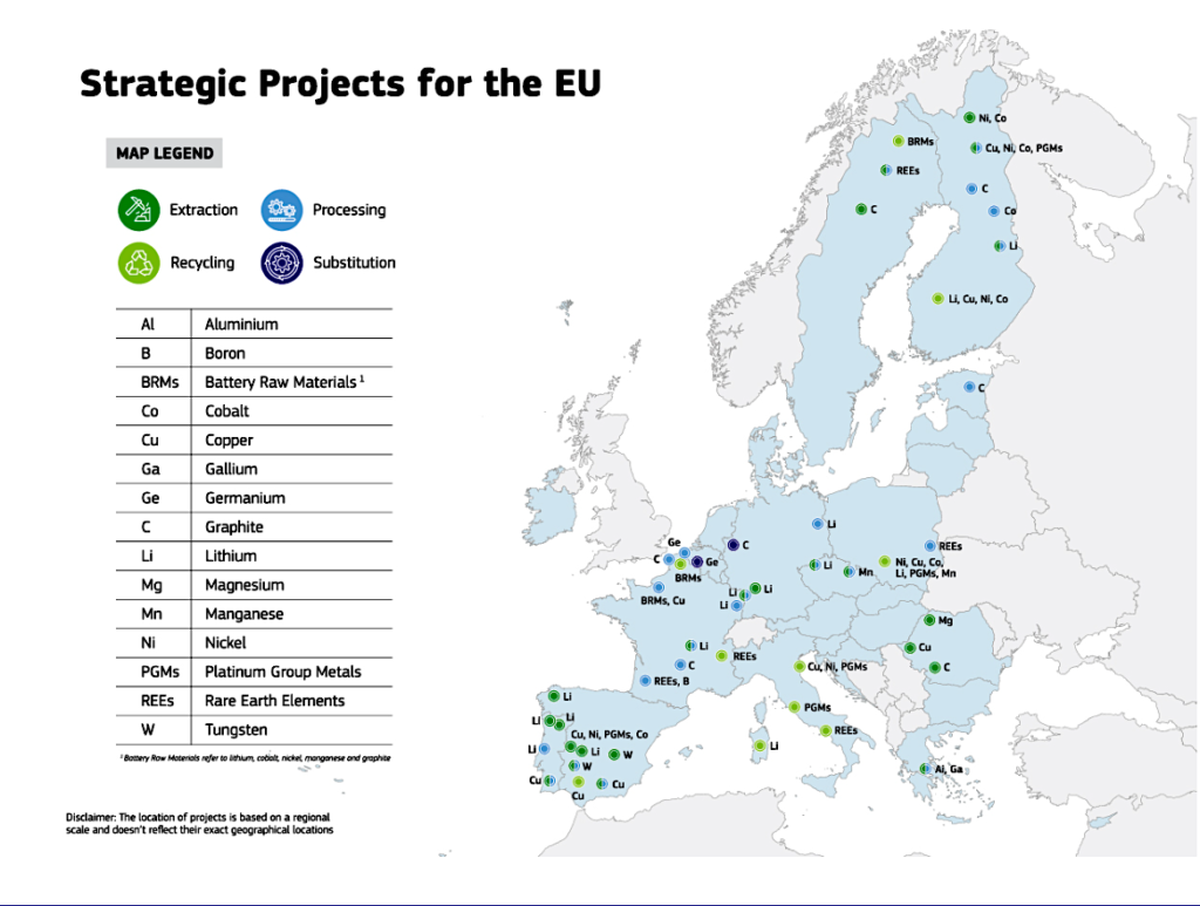
Europe’s strategic projects qualify for fast-track progression through the permitting stage – a maximum 27 months for mine projects and 15 months for processing projects – and access to funding both at European and national level.
The list is heavily weighted towards battery inputs such as lithium, cobalt, nickel and graphite but also includes more esoteric elements such as gallium, germanium and tungsten. Fourteen out of 17 metals on the EU’s strategic metals list are represented.
The projects across 13 member states extend along the whole length of the supply chain from mining to processing to recycling and even materials substitution.
They should allow the EU to fully meet its 2030 domestic production benchmarks for lithium and cobalt and make “substantial progress” for other battery materials such as nickel, manganese and graphite.
In the case of gallium, used in semi-conductors and currently subject to Chinese export restrictions, METLEN’s project in Greece will cover the region’s needs by 2028.
There is more to come.
The European Commission received 46 applications for projects outside of the EU. A decision on the potential selection of such projects “will be decided at a later stage,” it said.
Current crisis
Europe’s bold ambitions for new energy metals stand in stark contrast to the dire problems facing its traditional metals production sectors.
EU steel output has declined from 160 million metric tons in 2017 to 126 million in 2023. Current steel capacity utilization of around 65% is unsustainable, the Commission said.
The region has lost a significant part of its primary aluminum production capacity for good and around half of what remains has been idled since 2021.
The Commission’s “Action Plan” identifies high power costs as a core problem for its industrial metals base. Power prices surged in 2022 after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and although they have since fallen, they remain higher than historical levels and well above those in the United States.
A range of solutions is proposed from facilitating more long-term power supply contracts to improving network efficiency and accelerating permitting for building more renewable grid capacity.
In the short term member states are called “to rapidly implement and make use of all the flexibilities (of state aid rules) to lower costs for energy-intensive industries.”
Tariff turbulence
The threat of metal diverted from the United States washing up in Europe has focused minds on how to prevent further contraction in Europe’s steel and nonferrous metals sectors.
Tighter steel import quotas could come as soon as next month, according to European Commission Executive Vice-President Stephane Sejourne.
A “melted and poured” rule, allowing the Commission to take action against the original producer of the metal rather than a third-party transformer, is under consideration.
Plans for import restrictions on aluminum are being fast-tracked with the Commission gathering “relevant evidence” in preparation for some sort of safeguard measures.
This is a race against time for many struggling operators.
Paul Voss, Director General of European Aluminium, has called for “immediate, targeted interventions to stabilize the sector now.”
One of those interventions would be to stem the flow of recyclable materials out of Europe.
Scrap wars
Although the US tariffs of 25% on aluminum imports have been presented as “without exceptions of exemptions”, they do not apply to the movement of scrap.
Aluminum scrap exports from the EU were already on track to hit a record of 1.3 million tons last year. That figure is likely to rise this year as more material goes to the United States, where processors can remelt it into aluminum products and pocket the tariff premium.
European copper recyclers are similarly worried that the threat of US copper tariffs is already pulling more units to the United States along with refined metal.
The Commission is promising to propose by the third quarter of the year appropriate trade measures to ensure more scrap stays in the EU.
That will include reciprocal measures on both those countries applying metals tariffs and on those that currently block exports of scrap.
Global scrap trading has so far been largely unaffected by geopolitics but that looks about to change.
Sense of urgency
The European Union is playing catch-up with the United States, when it comes to investing in critical metals capacity.
But the 27-member bloc has no equivalent of the presidential powers used by both the Joe Biden and Trump administrations.
The combination of strategic projects and metals action plan shows that the European Commission has woken up to the urgency of both building for the future and protecting what it already has.
But as both corporates and lobby groups have been quick to point out, words need to be followed by action.
Or to quote Voss from European Aluminium, “strategy alone won’t keep our operations running.”
source: mining.com


Gold price edges up as market awaits Fed minutes, Powell speech

Glencore trader who led ill-fated battery recycling push to exit

Emirates Global Aluminium unit to exit Guinea after mine seized

Iron ore price dips on China blast furnace cuts, US trade restrictions

Roshel, Swebor partner to produce ballistic-grade steel in Canada

US hikes steel, aluminum tariffs on imported wind turbines, cranes, railcars

Trump weighs using $2 billion in CHIPS Act funding for critical minerals

EverMetal launches US-based critical metals recycling platform

Afghanistan says China seeks its participation in Belt and Road Initiative

Energy Fuels soars on Vulcan Elements partnership

Northern Dynasty sticks to proposal in battle to lift Pebble mine veto

Giustra-backed mining firm teams up with informal miners in Colombia

Critical Metals signs agreement to supply rare earth to US government-funded facility

China extends rare earth controls to imported material

Galan Lithium proceeds with $13M financing for Argentina project

Silver price touches $39 as market weighs rate cut outlook

First Quantum drops plan to sell stakes in Zambia copper mines

Ivanhoe advances Kamoa dewatering plan, plans forecasts

Texas factory gives Chinese copper firm an edge in tariff war

Energy Fuels soars on Vulcan Elements partnership

Northern Dynasty sticks to proposal in battle to lift Pebble mine veto

Giustra-backed mining firm teams up with informal miners in Colombia

Critical Metals signs agreement to supply rare earth to US government-funded facility

China extends rare earth controls to imported material

Galan Lithium proceeds with $13M financing for Argentina project

Silver price touches $39 as market weighs rate cut outlook

First Quantum drops plan to sell stakes in Zambia copper mines

Ivanhoe advances Kamoa dewatering plan, plans forecasts